Overview
Inkjet ink pigments are finely ground, insoluble particles dispersed in a liquid carrier for printing applications. Unlike dye inks—where colorants dissolve—pigment particles remain suspended, providing enhanced durability, lightfastness, and water resistance, making them essential for professional, archival, and industrial printing.
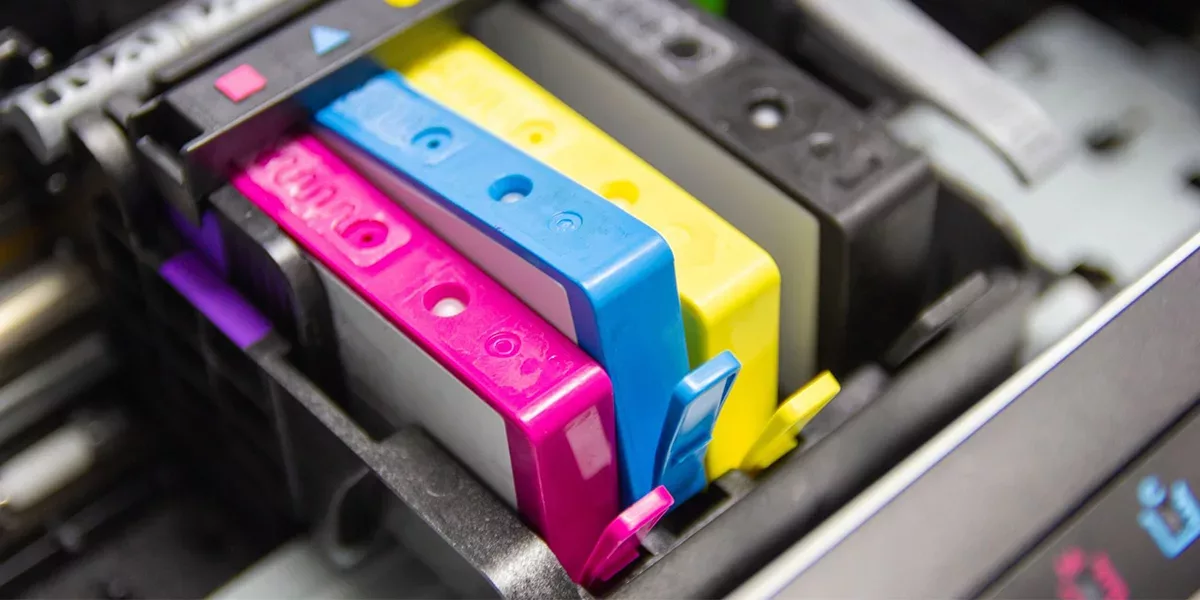

Composition
1. Pigment Particles
These consist of organic or inorganic solids such as carbon black, titanium dioxide, diarylide yellows, and quinacridone compounds. They are insoluble and remain on the surface of the printed material rather than penetrating it.
2. Liquid Carrier (Vehicle)
The carrier fluid is typically water-based (aqueous) or solvent-based and acts as the medium for transporting pigment particles through the print head and onto the substrate.
3. Resins and Binders
Resins such as acrylics or ketones help pigment particles adhere to surfaces, providing gloss, durability, and scratch resistance.
4. Additives
These include dispersants to prevent pigment clumping, surfactants to manage surface tension, humectants to retain moisture and avoid nozzle drying, biocides for shelf life, and defoamers to ensure smooth printing.
5. Extenders and Fillers
Inorganic materials can be added to adjust ink viscosity and reduce pigment load without impacting color intensity.
Particle Engineering & Dispersion
Pigment particles are ground down to nanoscale—typically around 100 nanometers—and uniformly dispersed in the carrier liquid. Advanced dispersing technologies and stabilizing agents ensure the particles remain suspended, preventing clogging and enabling smooth, vivid printing.
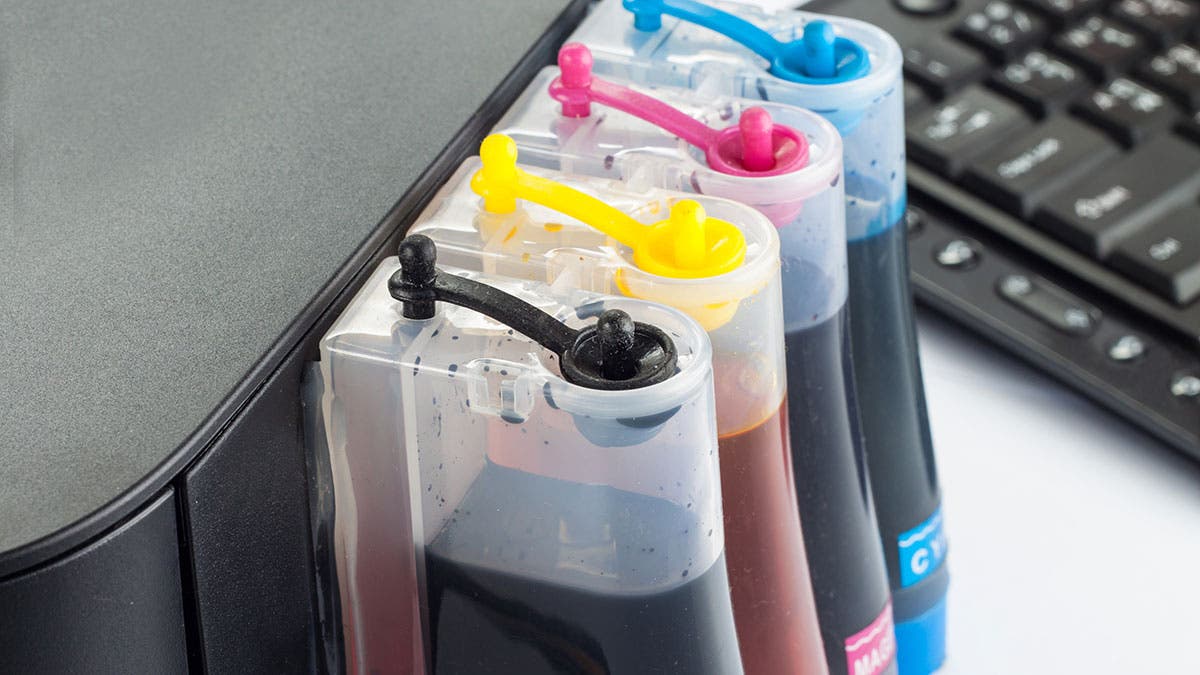

Types of Pigment Ink
Aqueous Pigment Inks
These are water-based and environmentally friendly. They are ideal for porous media such as photo paper, fine art prints, and labels. Aqueous pigment inks are known for their archival qualities and minimal volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions.
Solvent-Based Pigment Inks
These use organic solvents instead of water, making them suitable for printing on non-porous materials like vinyl and plastics. They are highly durable and weather-resistant, often used in outdoor signage and industrial labels.
Advantages
Durability & Resistance
Pigment inks offer excellent resistance to ultraviolet light, water, and physical abrasion. They are suitable for long-term and outdoor applications.
Archival Stability
Prints made with pigment inks can last decades without noticeable fading, making them ideal for photography, art reproduction, and documentation.
Printhead Compatibility
Properly formulated pigment inks do not clog print heads, which enhances printer reliability and reduces maintenance.
Limitations Compared to Dye Inks
Color Vividness
Pigment inks traditionally have a narrower color gamut and lower gloss compared to dye inks. However, recent advancements are closing this gap.
Cost
Pigment inks are generally more expensive due to complex formulation, nano-dispersion processes, and higher-quality ingredients.
Typical Applications
Fine Art and Photography
Pigment inks are widely used in high-end printing for photography, canvas, and museum-grade art prints due to their superior longevity and detail reproduction.
Outdoor and Industrial Printing
Thanks to their durability, pigment inks are perfect for signage, packaging, and durable labels that are exposed to environmental wear.
Textile and Heat Transfer Printing
With the right binders or fabric pretreatment, pigment inks can be used for textile printing, offering resistance to washing and sunlight.
Formulation and Quality Control
Physicochemical Standards
Manufacturers strictly control particle size, viscosity, surface tension, and other properties to ensure printing consistency and performance.
Performance Testing
Pigment inks undergo extensive tests for UV resistance, water fastness, scratch resistance, and adhesion to ensure they meet application demands.

Manufacturing Process
-
Raw Material Selection
Pigments, carriers, and additives are chosen based on desired print performance, substrate type, and environmental compliance. -
Nanoparticle Milling
Pigments are reduced to fine particles to enhance dispersion, color brightness, and uniformity. -
Additive Integration
Dispersants, humectants, binders, and other functional additives are blended into the formulation. -
Filtration
The ink is filtered to remove oversized particles that could clog printer nozzles. -
Quality Testing & Packaging
Inks are tested under real-use conditions and packaged in air-tight, UV-safe containers to preserve quality.
Future Trends
Advancements in nanoparticle pigment technology are pushing the boundaries of color vibrancy and gloss, previously limited to dye inks. Eco-friendly carriers and solvent alternatives are gaining traction as environmental regulations become stricter. Customized pigment ink systems for ceramics, electronics, and sustainable packaging are expanding the scope of applications.